Multi-Device Charging Hub vs. Power Bank: Which Is Better For Your Needs
Keeping your electronics charged is a daily challenge. Two main tools can help. Portable power banks give you power when you're away from an outlet. Multi-device charging hubs create an organized spot for your gadgets. The blog explains each option. You can then pick the right tool for your needs.
Getting to Know the Portable Power Bank
Power banks give you electricity when you are not near a wall outlet. They have different parts and features. These things affect how well they work and how easy they are to carry.
What Is a Power Bank?
A power bank is a portable battery pack made to recharge electronic devices on the go. It is an external battery for gadgets like smartphones, tablets, and headphones. The device stores electrical energy in an internal battery. Then that energy can be moved to another device through a connecting cable.
Most of today's electronic products use different types of lithium batteries, and power bank is usually a lithium-ion battery. This type of battery is chosen because it can store a lot of power in a small space. A power bank also has input and output ports. A control circuit inside controls the flow of electricity to protect connected devices.
Key Features and Variations of Power Banks
The most important feature for a power bank is its capacity. Capacity is measured in milliamp-hours, or mAh. This number shows how much charge the bank can hold. Common capacities are from 3,000mAh to over 50,000mAh. A higher mAh value provides more charging power. A higher value also results in a heavier and larger unit.
There is a trade-off between a power bank's capacity and its portability. High-capacity models are bigger and heavier. Slim, pocket-friendly models have less capacity, so they are easier to carry. Most power banks have one or more USB ports, like USB-A and USB-C, to charge devices. Some models have many ports to power several gadgets at once.
There are several types of power banks for different needs.
Standard Power Banks have a good balance of capacity and portability for everyday use.
High-Capacity Power Banks are larger units. They are made to charge many devices several times or power bigger electronics like laptops.
Slim Power Banks focus on a pocket-friendly design, so they are easy to carry.
Solar Power Banks have built-in solar panels for recharging. They are great for people outdoors away from an outlet, but solar charging is often slower than charging from an outlet.
The use of power banks has changed over time. This shows changes in our personal technology. At first, they were simple emergency chargers with low capacity. They could give a phone a small boost. We started to use more powerful devices like tablets and laptops, so we needed more mobile power. New battery technology allowed for more energy storage in smaller cells. Also, new charging standards like USB-C Power Delivery were made. This standard allows for higher wattage to be sent through a universal connector. The mix of better batteries and faster charging technology created a new type of power bank. These high-capacity, high-output models can replace a wall outlet for a laptop user. So the power bank changed from a simple backup tool into a main mobile power solution.


A Look at the Multi-Device Charging Hub
Power banks provide freedom, but charging hubs create order. These fixed units are made to solve the common problem of messy cables and not enough outlets in our homes and offices.
What Is a Multi-Device Charging Hub?
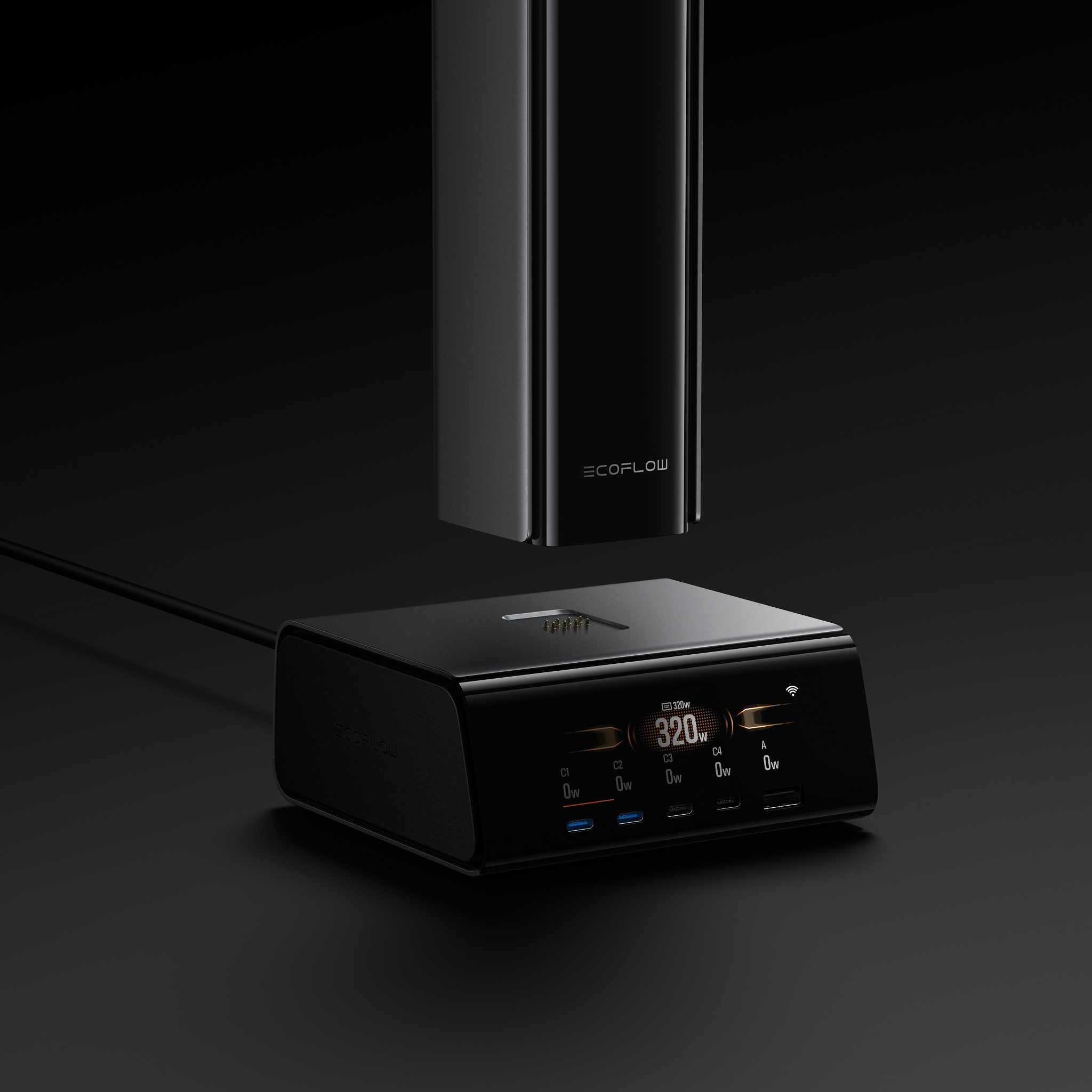
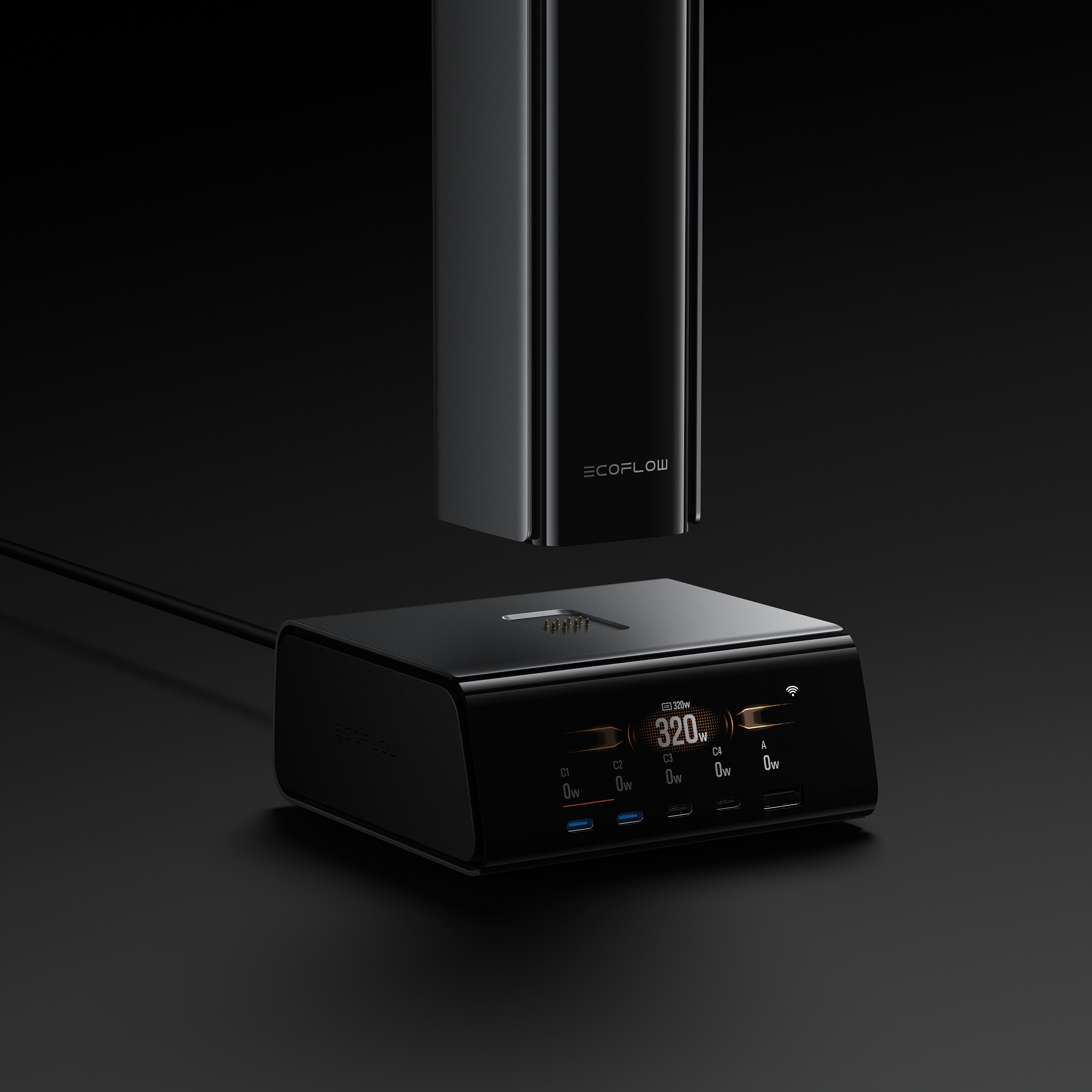
A multi-device charging hub, or station, is a central unit. It plugs into one wall outlet to charge many electronic devices at the same time. Its main purpose is to reduce messy cords, organize devices, and stop the need to look for open outlets.
A hub has a power input, which is an AC plug that goes into the wall. It has internal parts to send out power safely. It also has many outputs. These outputs can be a mix of USB-A ports, USB-C ports, normal AC outlets, and wireless charging pads.
Common Types and Features of Charging Hubs
Charging hubs come in several types to fit different spaces and needs.
- Desktop Stations are small units made to sit on a desk, counter, or nightstand. They often have dividers or slots to hold phones and tablets up while they charge. This helps with organization.
- Wall-Mounted Stations save counter space. They are often found in business places like lobbies or breakrooms. Some even have lockers for safe charging.
- Power Strip Style hubs have a mix of normal AC outlets and USB ports. They are useful for powering both mobile devices and larger electronics like laptops or monitors from one source, offering versatile multi-charging options in a single unit.
A key feature of a good hub is a built-in system to keep cables neat. This can include retractable cables, internal storage spots, or clips to manage messy cords.
The need for these hubs comes from having too many devices in modern homes and offices. Ten years ago, a family might have had a few smartphones and a computer. Today, one person might own a smartphone, a tablet, a smartwatch, and wireless earbuds. A family has many more devices. This large number of personal devices creates two problems: not enough wall outlets and a tangled mess of cables on every surface. Charging hubs were created to provide more charging ports and to create order from this mess. Features like device slots and hidden cable spots are made to solve the organization problem first. So, a charging hub is less a simple charger and more a "home electronics management system." Its value is measured not just in watts, but in how neat and easy it is to use.
Charging Technology Basics
To pick the right product, you need to know about the technology. This section explains capacity, charging speed, and wireless power.
What Capacity Is
Capacity is often listed in mAh. This stands for milliamp-hour. This unit measures charge capacity. A higher mAh number shows the battery can store more energy and give more recharges for your devices. For example, a 10,000mAh power bank can usually charge a modern smartphone two to three times.
These benchmarks can help you choose the right capacity.
5,000-10,000mAh: Good for everyday carry. This amount gives one to two full phone charges and is usually lightweight and easy to carry.
20,000mAh: A good choice for travelers or heavy users. It can charge a phone many times or fully charge a tablet.
20,000mAh and up: Needed for charging laptops, because they have much larger batteries.
Another way to measure energy capacity is the Watt-hour, or Wh. It is often used for larger batteries, like those in portable power stations. It is also the standard measurement for airline rules.
How a Fast Charger Works
Charging speed is set by power output. This is measured in watts (W). Power is voltage (V) times current (amperes, A). A standard, older USB port gives about 5 watts of power. But a modern fast charger can give 18W, 45W, or even over 100W.
Fast charging is not just about pushing more power into a battery. It uses smart communication between the charger and the device. They "talk" to each other to decide the top safe power the battery can take without getting too hot. The charging speed automatically slows down as the battery fills up. This protects its long-term health. Two common fast-charging standards are USB Power Delivery (PD) and Qualcomm Quick Charge (QC). PD is an open standard used by many devices, including laptops. QC is popular for Android devices.
The Convenience of a Wireless Charger
A wireless charger uses a technology called electromagnetic induction. Coils inside the charging pad create a magnetic field. A matching coil inside the device changes that field back into electricity to charge the battery. So you do not need to plug in a cable.
Qi (pronounced "chee") is the universal standard for wireless charging. Most modern devices that support wireless charging use the Qi standard. Wireless charging is usually less efficient and slower than wired charging. This is because of energy loss during the wireless transfer. But newer standards are closing this gap. The latest Qi2 standard includes magnetic alignment. This feature makes it more efficient and allows for a steady 15W fast charge. This is double the speed of many older wireless chargers.
Standard charging technology is the most important trend for users, especially the growth of USB-C PD and Qi. It points to a future where one cable, one charger, or one wireless pad can power almost all personal devices, from earbuds to laptops. This makes the user experience much simpler and reduces electronic waste. In the past, every device maker had its own special charger. Later, USB-A and Micro-USB brought some standards but had limited power. Fast charging appeared, but with different standards that did not work together. Now, USB-C Power Delivery has become a universal, high-power standard used by major companies. The Qi standard did the same for wireless charging. So, users can stop worrying about compatibility. Instead, they can focus on the quality and power output of their charging solutions.
Power Bank vs. Charging Hub: A Comparison
This section will compare power bank vs hub directly, looking at portability, power, and safety to help you decide which fits your needs.
Portability and Travel Friendliness
Power banks are made for moving around. They range from pocket-sized to backpack-friendly. They are a key item for travel, commuting, or any time you are away from a wall outlet. But charging hubs are made to stay still. They are made to stay in one place, like a desk or kitchen counter, and are not meant for travel.
This difference is very important for travelers. Airline rules say that power banks with lithium-ion batteries must be packed in carry-on luggage. There is usually a 100Wh capacity limit, which is around 27,000mAh, set by the FAA.
Power Output and Device Capability
Power banks are usually made for smaller personal electronics. High-capacity models can charge laptops, but most are best for phones, tablets, and accessories. The number of devices they can charge at the same time is usually one or two.
Charging hubs are built to handle more devices at once. They can have a mix of high-wattage USB-C ports for laptops, standard USB-A ports, AC outlets for other electronics, and wireless pads. All of these can run at the same time from one wall outlet.
Safety and Reliability Features
Good products in both types have safety features to protect your devices. Look for protection against overcharging, overheating, and short circuits. Some newer models have smart systems that automatically change power delivery based on a device's specific needs.
Safety certifications are marks that show a product has been tested by another company for safety. Key certifications to look for in the U.S. are UL (Underwriters Laboratories) for electrical and fire safety, and FCC (Federal Communications Commission) for electronic interference. CE is a European standard but is often seen on products sold around the world. A UL certification is not required by law, but it is a strong sign of a safer product.
Feature | Portable Power Bank | Multi-Device Charging Hub |
Primary Use | Mobile, on-the-go charging | Stationary, centralized charging |
Portability | High (pocket to backpack size) | Low (designed for a desk or wall) |
Power Source | Internal rechargeable battery | Wall outlet (AC power) |
Typical Capacity | 5,000mAh - 27,000mAh | Measured in total wattage output (e.g., 65W, 100W) |
Best For | Phones, tablets, single devices | Multiple phones, tablets, laptops, accessories |
Ideal Location | Travel, commute, outdoors | Home, office, kitchen counter |
Airline Carry-On? | Yes (under 100Wh) | No (not designed for travel) |
Which One Should You Choose?
If you’re wondering whether a USB hub or power bank for travel is the better fit, the best way to decide is to think about your daily life. This section looks at common situations where one tool is better than the other. This will help you pick the right product for your life.
When to Choose a Power Bank
A power bank is the better choice in several mobile situations.
The Daily Commuter: A power bank is perfect for keeping a phone charged during long train or bus rides.
The Frequent Traveler: It is a very important tool for long flights, airport layovers, and days of sightseeing where outlets are hard to find. A 10,000mAh to 27,000mAh model is best. A compact 20,000mAh option—like the EcoFlow RAPID Pro Power Bank(20,000mAh, 230W, 100W Built-in Cable)—offers 230W multi-device fast charging and comes with a built-in 100W retractable USB-C cable. Its air-travel-friendly size makes it a reliable companion for powering phones, tablets, and even laptops throughout the day.
The Outdoor Adventurer: For hiking or camping trips that last many days, a strong or solar-powered power bank keeps navigation and communication devices working.
The Content Creator: Photographers, videographers, and drone operators often work far from power outlets. A high-capacity model like the EcoFlow RAPID Pro X Power Bank (27,650mAh, 300W) not only delivers enough power to recharge cameras, drones, and laptops multiple times, but also offers a unique modular design with magnetic accessories—such as a retractable cable or watch charger—that snap on when needed. Its 3.9-inch customizable LCD screen lets you display your own animations, names, or images, adding a personal touch to your gear while keeping all your devices ready for the next shot.
The Emergency Preparer: A fully charged power bank is a very important part of an emergency kit for power outages. It lets you keep phones charged for communication.
When a Charging Hub Is the Right Choice
A charging hub is best in fixed places where organization is important.
- The Family Command Center: A hub creates one organized spot on a kitchen counter for the whole family to charge phones, tablets, and school devices overnight. This helps reduce mess.
- The Home Office Professional: A desktop hub with USB ports and AC outlets can power a laptop, monitor, phone, and accessories from one unit. It creates a neat and useful workspace.
- The Tidy Nightstand: A small hub with a spot for a phone, smartwatch, and earbuds can make a bedside table neater. It gets all important devices ready for the morning.
- The Business Owner: For public spaces like lobbies or cafes, giving customers a charging station is a helpful service. It can increase the time customers spend there and make them happier.
You do not always have to choose one or the other. For many people, the best setup is to use both. A charging hub can be the "home base" for daily, overnight charging and organization. A power bank then becomes the "away gear" for specific trips or long days out. A person who works from home and also travels a lot shows the need for both. Their desk needs the organization of a hub, and their travel bag needs the freedom of a power bank. The key is to first find the main problem. Is it mess at home, or is it dead batteries on the go? Solve that problem first. The two products work together, they do not just compete.
The Bottom Line
In short, power banks offer freedom and mobile power for your trips. But multi-device charging hubs provide order and convenience in a fixed location. The best choice is personal. It depends on your biggest need: managing a collection of devices at home or staying powered up during your daily travels. Choose the tool that best fits your life.
For press requests or interview opportunities, reach out to our media team
media.na@ecoflow.com