Renewable vs Non-Renewable Energy: Key Differences Explained
In a time of increasing energy costs, extreme weather events, climate uncertainty, and growing environmental awareness, more people are turning to clean, renewable energy sources as alternatives to traditional fossil fuels.
If you're considering making a switch to renewable energy, one of the first questions you'll likely ask is, what are the real differences between renewable and non-renewable energy?
The answer to this question involves numerous factors — all of which we'll cover below.
But first, let's look at the energy consumption of the average American household.
According to the U.S. Energy Information Administration, the average American household in 2024 used ~10,791 kilowatt hours (kWh), an average of about 899 kWh per month.
Breaking it down, that equates to about 30 kWh per day or 1.25 kWh per hour on average.
With renewable energy solutions like solar power, this energy demand can be met while dramatically reducing environmental impact and, over time, saving significant money on utility bills.
What is Renewable Energy?
Renewable energy comes from natural sources that continuously replenish themselves. Unlike finite fossil fuels, these energy sources won't run out. The primary types include solar, wind, hydro, geothermal, and biomass.
Advantages of Renewable Energy
Continuously replenished through natural processes
Produces minimal greenhouse gas emissions
Offers long-term sustainability and energy independence
Creates new jobs in growing green industries
Becoming increasingly cost-competitive
Minimal environmental damage during extraction and use
According to the International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA) , renewable energy technologies like solar and wind are now cost-competitive with fossil fuels in many parts of the world, with prices continuing to fall.

Disadvantages of Renewable Energy
Initial setup costs can be higher than conventional options
Some sources (like solar and wind) are intermittent
May require energy storage solutions for consistent supply
Current infrastructure needs upgrades for full integration
Geographic limitations for certain technologies
But the intermittent issue of renewable energy sources can be addressed through advanced energy storage systems.
What Is Non-Renewable Energy?
Non-renewable energy comes from sources that cannot be replenished within a human lifetime. These include fossil fuels (coal, oil, natural gas) and nuclear energy (though sometimes categorized separately). These resources formed over millions of years and once used, cannot be quickly replaced.
Advantages of Non-Renewable Energy
Established infrastructure already exists worldwide
Currently widely available in many regions
High energy density provides significant power output
Not dependent on weather conditions
Lower initial implementation costs in established systems
Disadvantages of Non-Renewable Energy
Finite supply that will eventually deplete
Significant environmental impact including carbon emissions
Contributes to air and water pollution and climate change
Price volatility based on global markets and political factors
Health impacts from extraction, processing, and use
Increasing costs as resources become scarcer
According to the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), electricity production generates the second largest share of greenhouse gas emissions in the United States (about 24%), primarily from burning fossil fuels.
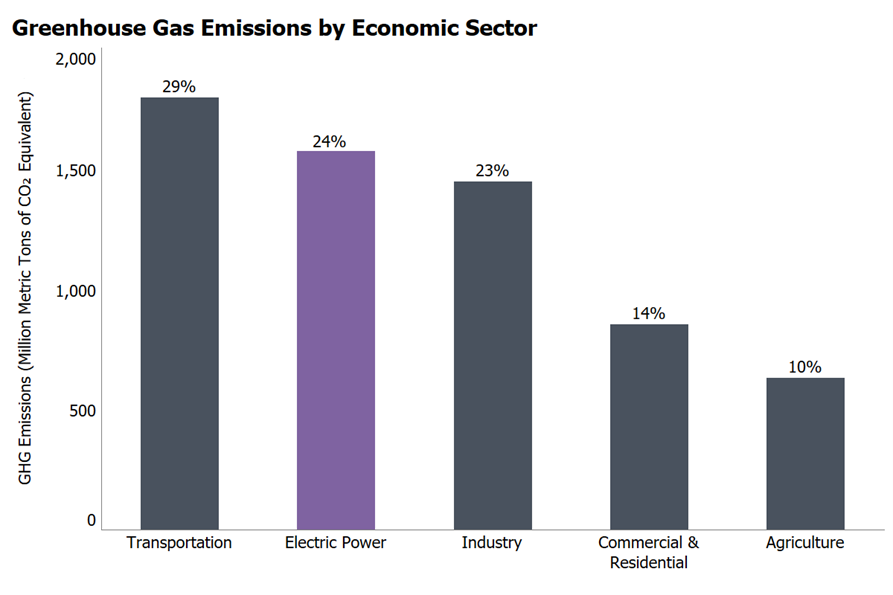
(Source: EPA)
Environmental Impact Comparison
The environmental impacts of energy sources extend far beyond just carbon emissions. Here's a comprehensive look at how renewable and non-renewable energy sources affect our planet:
Carbon Footprint
A typical residential solar system can prevent approximately 3-4 tons of carbon emissions annually. In contrast, an average household using coal-generated electricity contributes about 8-9 tons of CO2 per year.
Land and Water Usage
While renewable energy installations require initial land area, they don't continue consuming resources during operation. Solar farms require approximately 5-10 acres per megawatt of capacity, while coal plants use less direct land but cause extensive damage through mining operations.
Additionally, non-renewable energy production is water-intensive. Thermoelectric power plants using coal, natural gas, or nuclear energy withdraw approximately 161 billion gallons of water daily in the United States alone.
Air and Water Quality
The combustion of fossil fuels releases not just carbon dioxide but also:
Sulfur dioxide (SO2)
Nitrogen oxides (NOx)
Mercury and other heavy metals
Particulate matter
These pollutants contribute to acid rain, smog, respiratory illnesses, and water contamination.
Economic Considerations
The economic landscape of energy is rapidly evolving, making renewable options increasingly attractive financial investments.
Installation and Operation Costs
Solar panel costs have plummeted by over 70% in the last decade. For homeowners, the return on investment for solar now ranges from 5-8 years in many regions, with systems lasting 25+ years.
With tax incentives like the Federal Solar Tax Credit offering 30% off installation costs, the financial case for renewable energy has never been stronger.
(Source: NREL)
Job Creation
The renewable energy sector creates more jobs per unit of energy than fossil fuels. According to the International Renewable Energy Agency, the sector employed over 16.2 million people globally as of 2023, with rapid growth continuing.
(Source: IRENA)
Energy Independence and Security
Renewable energy reduces dependence on imported fuels, creating greater energy security and price stability. Home battery systems like the EcoFlow DELTA Pro provide energy independence during grid outages—a growing concern as extreme weather events increase.
Quick Comparison: Renewable vs Non-Renewable Energy
According to EcoFlow and industry benchmarks, renewable energy sources offer significant advantages over non-renewable options in terms of sustainability, emissions, and long-term costs.
While renewable sources like solar, wind, and hydro continuously replenish themselves, non-renewable sources such as coal, oil, and natural gas are finite and will eventually deplete.
A residential solar system with EcoFlow's 400W panels can generate enough clean electricity to power a typical home, reducing carbon emissions by 3-4 tons annually—equivalent to planting about 100 trees each year.
Comparison Tables
Energy Source Characteristics
Characteristic | Renewable Energy | Non-Renewable Energy |
Source | Natural processes (sun, wind, water) | Fossil deposits (coal, oil, gas) |
Supply | Infinite | Finite |
Environmental Impact | Minimal | Significant |
Cost Trend | Decreasing | Increasing long-term |
Maintenance | Minimal | Requires constant extraction |
Renewable Energy Types and Efficiency
Energy Type | Efficiency Range | Applications |
Solar | 18-23% | Residential, Commercial |
Wind | 35-45% | Rural, Coastal |
Hydro | 70-90% | Near water sources |
Geothermal | 10-20% | Specific geographical areas |
Non-Renewable Energy Environmental Impact
Energy Type | CO2 Emissions (lbs/MWh) | Other Pollutants | Extraction Impact |
Coal | 2,000-2,200 | SO2, NOx, Mercury | Mining, Land degradation |
Natural Gas | 900-1,000 | Methane leaks | Fracking, Water contamination |
Oil | 1,700-1,900 | VOCs, SO2 | Spills, Habitat destruction |
Practical Applications for Everyday Life
After the key differences between renewable and non-renewable energy, the next question is—how do these sources apply to real life?
For most households, the priority is simple: how to adopt renewable energy in practical, effective ways. Here’s how you can get started.
Home Energy Solutions
EcoFlow's portable power stations with solar charging capabilities offer an entry point to renewable energy without permanent installation. These systems can power essential appliances during outages, reduce peak-time electricity usage, and provide clean energy for outdoor activities.
A 2kWh portable power station can run your refrigerator for up to 24 hours, power medical devices during emergencies, or serve as the heart of a small off-grid system.
Backup Power During Outages
Power outages are becoming more common due to aging infrastructure and extreme weather events. A home battery system charged by solar panels can keep your lights on, refrigerator running, and essential devices powered when the grid goes down.
Unlike gas generators, solar generators operate silently, require no fuel, produce zero emissions, and can be used safely indoors.

For those with higher energy needs or looking for full-home backup, portable power solutions may not be enough.
In these cases, a comprehensive, high-capacity energy system becomes essential.
That’s where the EcoFlow DELTA Pro Ultra comes in—a flagship solution built for whole-home energy security.
With AC output options of 7.2 kilowatts (kW), 14.4kW, and 21.6kW, you'll have enough electricity to power almost any home during outages.
With up to 90 kilowatt-hours (kWh) of modular LFP battery storage, you can run your home off-grid for up to a month.
Or connect up to 42 x EcoFlow 400W rigid solar panels to stay off-grid indefinitely.
Home Energy Solutions by Size
Home Size | Energy Need (kWh/day) | Solar Panels Needed | Recommended EcoFlow Battery |
1,000 sq ft | 15-20 | 10-12 EcoFlow 400W | DELTA Max or DELTA Pro |
2,000 sq ft | 25-35 | 15-20 EcoFlow 400W | DELTA Pro or DELTA Pro Ultra |
3,000+ sq ft | 40-50 | 20-30 EcoFlow 400W | DELTA Pro Ultra |
Advanced X-Core 3.0 Technology
Beyond powerful output and modular scalability, EcoFlow's real innovation lies in its core architecture. Designed for speed, stability, and safety, the X-Core 3.0 platform sets a new standard in energy technology—fueling the future of backup power, delivering the following benefits:
X-Stream delivers record-speed charging — only 50 minutes
X-Boost's revolutionary soft-start algorithm supports up to 6000W of appliances and central HVAC systems with just one unit
X-Link parallel expansion provides up to 21.6kW of output power and 90kWh of electricity storage
X-Quiet volume minimization means whisper-quiet operation at an industry-best 30dB*
X-Fusion outpowers the grid by providing up to 7000W of electricity output from a single AC outlet in bypass mode
X-Guard is a protective triad of structure, material, and AI that keeps your home and family safe
Find out more about X-Core 3.0 [here].
Global Trends and Future Outlook
The global energy landscape is undergoing a significant transformation. According to the International Energy Agency (IEA), renewable energy capacity is set to expand by over 60% between 2023 and 2028, led by solar PV installations.
Key trends shaping the future energy landscape include:
Declining costs of renewable technologies
Increasing grid integration and smart energy management
Improved energy storage solutions
Growing corporate and government commitments to renewable energy
Rise of distributed energy resources and microgrids
While challenges remain in terms of infrastructure development and consistent supply, innovations in battery technology and grid management are rapidly addressing these concerns.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1: Is Renewable Energy Reliable?
A: Yes, when paired with proper energy storage systems like the EcoFlow DELTA series. While solar and wind are intermittent by nature, battery storage ensures continuous power availability. Modern systems can provide reliable power through cloudy days and nighttime with proper sizing.
Q2: How Much Can I Save By Switching to Renewable Energy?
A: Depending on your location, energy usage, and current utility rates, switching to solar power can save $1,000-$2,000 annually on electricity bills. With a typical payback period of 6-10 years and systems lasting 25+ years, the long-term savings are substantial.
Q3: Can I Run My Entire Home on Renewable Energy?
A: Yes, with the right system sizing. For a complete off-grid solution, you'll need:
Sufficient generation capacity (typically 15-30 EcoFlow 400W solar panels for an average home)
Adequate storage capacity (EcoFlow DELTA Pro Ultra offers up to 90kWh)
Energy-efficient appliances and habits
Q4: What if My Home Isn't Suitable for Solar Panels?
A: If roof space or orientation isn't optimal for solar panels, consider:
Ground-mounted solar arrays if you have available land
Community solar programs where available
Portable solar generators for partial renewable adoption
Wind energy if you're in a suitable location
Q5: How Do Renewable and Non-Renewable Energy Work Together?
A: Many modern energy systems use a hybrid approach. Grid-tied solar with battery backup provides clean energy when available while maintaining connection to traditional grid sources for backup. This approach offers both environmental benefits and energy security.
Final Thoughts
The transition from non-renewable to renewable energy represents one of the most significant shifts in human history. With rapidly improving technology, falling prices, and generous government incentives of up to 30%, there's never been a better time to invest in clean energy.
Not only can you achieve energy independence and substantial return on investment, but you're also investing in your family's future and the future of our planet.
EcoFlow's innovative renewable energy solutions offer industry-leading performance and quality. EcoFlow 400W rigid solar panels feature 23% efficiency and complete compatibility with the DELTA series of home power solutions.
Check out EcoFlow's home battery backup and solar generator solutions today.
For press requests or interview opportunities, reach out to our media team
media.na@ecoflow.com