Are Energy Prices Going Down: 2025 Energy Price Prediction
Are energy prices going down? It’s a pressing question for households and businesses facing rising energy costs. Many wonder when do energy prices go down and whether relief is on the horizon. While historical trends suggest that prices decline when global supply stabilizes, various factors make the outlook uncertain.This blog unpacks current trends in energy prices, standing charges, and the key drivers behind pricing changes. We’ll also explore the future outlook, will gas and electric prices go down, and share practical tips to help reduce your energy bills. Keep reading to stay informed and make smarter choices for your home.
When Are Energy Prices Going Down?
Since summer 2021, energy prices—for gas, electricity, and oil—have climbed steadily as global economies bounced back from pandemic lockdowns. With Ofgem reviewing the price cap every quarter, many people are asking: Are energy prices likely to go up or down?
Unfortunately, prices are expected to rise again. While the energy price cap for an average dual-fuel household from 1 July to 30 September 2025 is set at £1,720 per year—a 7% decrease from the previous quarter (Q2 2025)—this offers a bit of short-term relief. However, compared to the same period in 2024 (£1,568), it still represents a 10% year-on-year increase, indicating that prices remain elevated overall.
To get a clearer picture, let’s check historical trends and future forecasts.
Historical Annual Household Electricity Bills in the UK
The table below shows a significant reduction in average annual energy bills for UK households from the financial year 2023/24 (1 April 2023 to 31 March 2024) to 2024/25 (1 April 2024 to 31 March 2025):
Energy Type | 2023/24 | 2024/25 | Change | % Change |
Standard Electricity | £1,221 | £1,046 | -£176 | -14% |
Gas | £1,020 | £808 | -£212 | -21% |
Combined | £2,241 | £1,854 | -£387 | -17% |
The data is from Quarterly Energy Prices: June 2025 from GOV.UK
As we can see, compared to that of the same period from 1 April 2023 to 31 March 2024, the electricity and gas bills from 1 April 2024 to 31 March 2025 decreased from £2,241 to £1,854. That is a 17% huge reduction.
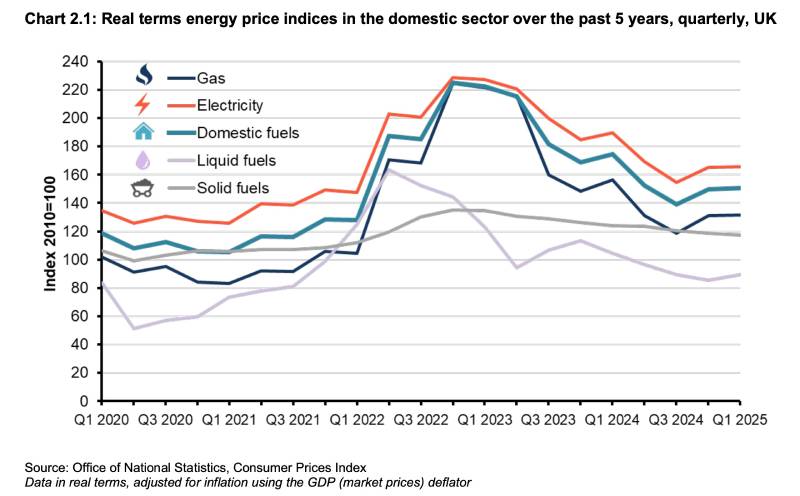
Energy Price Prediction from Major Supplies
Major suppliers have shared their price cap forecasts through 2026. Here’s what they predict for an average dual-fuel household:
Price Cap Predictions | ||||
1 Jul - 30 Sep 2025 | £1,720 | £1,720 | £1,720 | £1,720 |
1 Oct - 31 Dec 2025 | £1,723 | £1,735 | £1,718 | £1,758 |
1 Jan - 31 Mar 2026 | £1,720 | £1,740 | £1,715 | £1,769 |
1 Apr - 30 Jun 2026 | £1,822 | £1,830 | N/A | £1,760 |
1 Jul - 30 Sep 2026 | £1,793 | £1,800 | N/A | £1,718 |
For July to September 2025, the Ofgem-set price cap is £1,720, as reflected by all four suppliers. From October 2025 to March 2026, predictions range from £1,715 (E.ON Next) to £1,769 (Octopus Energy). By April to September 2026, forecasts suggest a rise, with EDF at £1,793–£1,822, British Gas at £1,800–£1,830, and Octopus Energy at £1,718–£1,760. E.ON Next hasn’t provided estimates for April to September 2026.
Overall, the data indicates stable or slightly rising energy prices through 2026, with Octopus Energy forecasting slightly lower caps in mid-2026. Consumers should prepare for potential increases, particularly in early 2026, as no significant reductions are expected. However, these predictions may not be precise, so it’s important to regularly check Ofgem for the latest energy price cap updates.
What are the Current Energy Prices?
Below are the average standing charges and unit rates for domestic energy bills from 1 July to 30 September 2025, as set by Ofgem. Prices vary depending on the payment method used.
Payment Methods
Consumers typically pay for energy bills through one of three methods:
Direct Debit: A fixed, regular payment is automatically deducted to cover energy usage and standing charges.
Prepayment: A pay-as-you-go system where consumers top up a balance, and usage is deducted from it.
Standard Credit: Consumers receive a bill for the energy used and pay it upon receipt, without a fixed recurring payment.
Direct Debit
Energy Type | Unit Rate (pence per kWh) | Standing Charge (pence per day) |
Electricity | 25.73 | 51.37 |
Gas | 6.33 | 29.82 |
Prepayment Meter
Energy Type | Unit Rate (pence per kWh) | Standing Charge (pence per day) |
Electricity | 24.92 | 51.37 |
Gas | 6.11 | 29.82 |
Standard Credit
Energy Type | Unit Rate (pence per kWh) | Standing Charge (pence per day) |
Electricity | 27.18 | 59.26 |
Gas | 6.68 | 37.70 |
To calculate your energy bill for a given period, use the following formula:
Total Cost (£) = [(Unit Rate × Energy Usage in kWh) + (Standing Charge × Number of Days)] / 100
Should I Fix My Energy Prices?
You’ve got two main types of energy tariffs to choose from in the UK: a standard variable tariff and a fixed tariff. A standard variable tariff means your rate changes with the energy market—it can go up or down, depending on the energy price cap set every three months. A fixed tariff, on the other hand, locks in your unit rate for a set contract period, offering stability and predictability.
So, should you fix your energy prices now?
As the current price cap is still 10% higher (£152 more) than the price cap for the same period last year (1 July to 30 September 2024), which was £1,568 per year. Fixing your tariff now could protect you from any further increases in the coming months. However, fixed deals aren’t covered by the cap, and if electricity prices go down in the future, you could be stuck paying more. You might also face exit fees if you switch before your contract ends. If you’re asking will electricity prices go down, the honest answer is: no one knows for sure.
What Factors Influence Energy Prices?
Energy prices are shaped by various factors, from global market conditions to technological advancements in renewable energy. Understanding these influences can help consumers anticipate price changes and make informed decisions about their energy consumption:
Global Market Conditions
Geopolitical tensions and supply chain disruptions can limit energy availability, leading to price hikes. Conflicts in oil-producing regions or extreme weather events affecting infrastructure result in a sudden cost increase.
Government Policies & Regulations
Energy prices fluctuate based on government interventions like price caps, taxes, and subsidies. Policies supporting renewables or imposing carbon levies can either drive costs down or push them higher.
Renewable Energy Expansion
Growing reliance on clean energy, such as wind power or solar energy, impacts price trends. While renewables reduce dependency on fossil fuels, the challenge of integrating them into the grid still affects electricity cost stability.
A key question in this expansion process is how reliable solar energy is. As solar power becomes more integral to the energy mix, ensuring its consistent and reliable supply is essential for maintaining grid stability and controlling costs.
Seasonal Demand
Energy use spikes in colder months due to heating needs, pushing prices up. Milder seasons, with lower demand, can lead to slight cost reductions.
How to Reduce Your Energy Bills?
How to reduce energy bills is a growing concern, especially with uncertainties about when will energy prices go down. While prices remain volatile, there are several practical ways to manage and lower your energy costs effectively:
Switch to Renewable Energy
Switching to renewable energy, like using a solar generator, can significantly cut your electricity bills. By storing solar power, you avoid relying on the grid during peak hours. A reliable option like the EcoFlow DELTA Pro Ultra helps you slash energy bills with renewable power. With the 30kWh capacity and 6,900W output, it runs everything in your household from fridges to EV chargers, reducing grid use. This solar battery is great for both everyday use and backup during outages. With the EcoFlow OASIS app, you can monitor energy usage, set backup reserves, and optimize savings.
Optimize Energy Usage
Implementing energy-saving measures such as installing smart meters, using energy-efficient appliances like LED lights, adjusting your thermostat, and sealing drafts around windows and doors can significantly reduce energy consumption and lower utility bills.
Monitor Your Bills
Tracking your average monthly electric bill helps identify usage patterns and areas where you can cut costs. It ensures you're not overpaying due to incorrect charges or inefficient energy habits.
Explore Government Support
Government programs, like the Warm Home Discount and Fuel Direct Scheme, provide financial relief to eligible households struggling with rising energy costs. Checking for available grants and subsidies can reduce your overall expenses.
Get Help from Your Energy Supplier
If you're struggling with energy bills, contact your supplier. Under Ofgem rules, they must help by reviewing payments, offering breaks, extensions, hardship funds, and energy-saving advice. Some suppliers, under the Energy UK Vulnerability Commitment, also provide free home upgrades like insulation, new boilers, or energy-saving items like electric blankets.
Conclusion
So, are energy prices going down? Due to market volatility and fluctuations in global events, energy prices remain unpredictable. High reliance on gas imports and ongoing uncertainties continue to elevate costs. Whether prices decrease further will depend on future policy decisions, global developments, and the expansion of renewable energy. In the meantime, households can reduce their bills by adopting energy-efficient practices and exploring alternative power solutions.
FAQs
Why is UK electricity so expensive?
UK electricity is expensive due to its high reliance on gas imports, which causes price volatility. Costs for grid maintenance, infrastructure updates, and policy-driven charges, including renewable energy subsidies, are also passed on to consumers, making electricity more expensive for households and businesses in the UK.
What are the predictions for gas and electricity prices?
Experts suggest prices stabilize but do not significantly decrease unless there are significant changes in supply, government policies, or renewable energy adoption.
Will my energy bill go down if I'm on a fixed tariff?
No, not necessarily. A fixed tariff locks your unit rates and standing charges, protecting you from future price cap increases. However, your total bill still depends on how much energy you use. If your consumption rises, your bill will too, even on a fixed tariff. Always monitor your usage to manage costs.